Sharing Data Between Host and Virtual Machine using Thunar and the ‘S’ commands (ssh,scp,sftp)
1. Introduction
Sharing a common folder or copying files between a host and virtual machine offers several benefits.
It allows for seamless data transfer, collaboration, and synchronization between the two systems. By sharing files or folders, both the host and virtual machine can access and modify files, thus enhancing productivity and convenience.
Here I put my focus on using the S commands
2. Using the scp command
One of the most commonly used and secure methods for file transfer in Linux is the scp (secure copy) command.
The following provides guidance on using scp to transfer files safely between the host and guest.
Before using scp for file transfer, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
a. Both the host and guest machines should have SSH (Secure Shell) installed and properly configured.
b. SSH server should be running on the host and guest machines
1. Transferring Files from Host to Guest:
From a command line terminal in the host:
scp [options] source_file user@guest_ip:destination_directory
Replace [options] with any desired options, such as specifying a different port (see man pages for that).
Replace source_file with the path and filename of the file you want to transfer from the host.
Replace user with the username on the guest machine.
Replace guest_ip with the IP address or hostname of the guest machine.
Replace destination_directory with the directory path on the guest machine where you want to save the transferred file.
-r Recursively copy entire directories
example:
scp /home/rosika/Dokumente/shared_folder/test.txt rosika2@192.168.122.174:/home/rosika2/tests
2. Transferring Files from Guest to Host:
From a command line terminal in the guest:
scp [options] source_file user@host_ip:destination_directory
Replace [options] with any desired options.
Replace source_file with the path and filename of the file you want to transfer from the guest.
Replace user with the username on the host machine.
Replace host_ip with the IP address or hostname of the host machine.
Replace destination_directory with the directory path on the host machine where you want to save the transferred file.
example:
scp /home/rosika2/tests/test_in-other-direction.txt rosika@192.168.8.102:/home/rosika/Dokumente/shared_folder
Note:
Enter the SSH password for the host machine when prompted.
There may be requests like these:
the authenticity of host ‘192.168.8.102 (192.168.8.102)’ can’t be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256: […]
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added ‘192.168.8.102’ (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
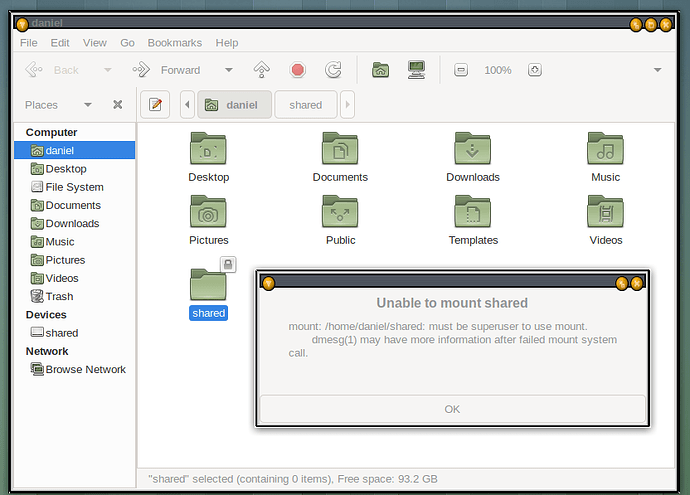
3. Using the file manager thunar for Sharing
Thunar, the file manager, which should already be installed on the host system, can also be utilized to access the virtual machine through SSH and perform file operations:
a) Launch Thunar on the host system
b) In the address bar, enter the following: ssh://username@virtual_machine_ip_address
(replace username with the username of the virtual machine and
replace virtual_machine_ip_address with the IP address of the virtual machine.)
You can get the IP address of the VM with ip a (from within the VM).
c) Authenticate by entering the password for the virtual machine when prompted.
d) Thunar will display the contents of the virtual machine’s file system, allowing file transfer and management between the host and virtual machine.
e) For convenience (and if used regularly) it might be a good idea to provide a bookmark to the VM in thunar.
f) Thunar lists the running VM under “network” in its left-side pane. It also has an eject button. It surely won´t hurt to “eject” the device when you don´t need the SSH connection anymore.
One can also use the ssh command directly at the command line in either host or guest, in the same manner as scp. This is of limited use. It allows you to browse files and to use copy/paste.
4. Sharing files and folders with the sftp command
In addition to scp, the sftp command can be used to establish an interactive file transfer session between the host and the virtual machine.
This allows for seamless transfer of files and folders using the secure FTP protocol:
a) Open a terminal on the host system
b) Connect to the virtual machine using sftp: sftp username@virtual_machine_ip_address
(replace username with the username of the virtual machine and
replace virtual_machine_ip_address with the IP address of the virtual machine.)
c) Enter the password for the virtual machine when prompted to establish the sftp connection.
d) Once connected, you can navigate the local host system using commands such as cd, ls, and pwd.
Use help to provide an overview of available commands.
Use bye or exit to quit sftp.
e ) To transfer files or folders from the host to the virtual machine (put command), use the following:
put /path/to/local/file_or_folder /path/to/remote/directory
put -r will be needed for folders (recursive put and get).
f) To transfer files or folders from the virtual machine to the host (get command), use the following :
get /path/to/remote/file_or_folder /path/to/local/directory
g) After executing the put or get command, sftp will initiate the file transfer between the systems. Progress will even be displayed in the terminal until the transfer is complete.
5. Recommendation
Use Thunar to drive SSH if you want a graphic interface to file sharing.
Use scp or sftp at the command line to copy files and folders between host and virtual machine. Use ssh at the command line if you just want to browse files or do copy/paste.
6. Links